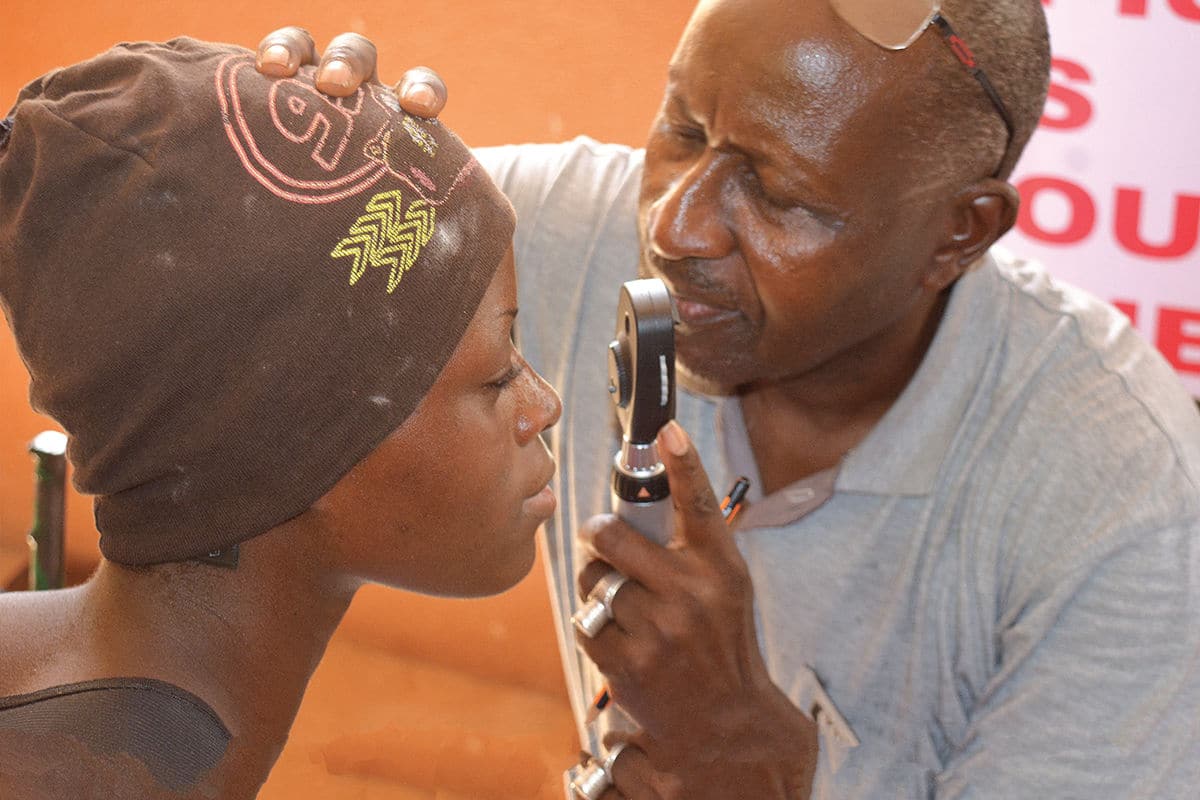

Cataract is an eye disease in which the lens of the eye becomes progressively more opaque, resulting in blurred vision. Cataract is the largest cause of blindness in the world. According to the IAPB Vision Atlas 2020, 100 million people have cataract. Of these, 17 million people are blind and 83 million experience vision impairment, with rates of vision impairment and blindness higher in women than men.
Cataract causes include aging, cortisone medication, diabetes, trauma and many others.
Symptoms of cataract include pinpoint vision and a feeling of continual fog that can go as far as blindness.
Cataract is diagnosed through eye tests, including visual acuity and retinal exams.
Sight can be restored with cataract surgery. The cataract surgeon removes the opaque lens and replace it with an artificial intraocular lens.
Francophone Africa is frequently overlooked by international development stakeholders when it comes to restoring sight and providing quality eye care. The Organization for the Prevention of Blindness (OPC) works with local governments, civil society organizations and communities to fight blindness, restore vision, encourage local ownership of eye health care systems and ensure human right to sight.






